OBJECTIVE
OF THIS TOPIC
1. Describe
the characteristics and uses of desktops, laptops, tablets, and handheld
computers
2. Describe
the characteristics and types of servers
3. Differentiate
among POS terminals, ATMs, and self-service kiosks
4. Describe
cloud computing and identify its uses
5. Describe
the characteristics and uses of smartphones, digital cameras, portable media
players, and e-book readers
6. Describe
the characteristics of and ways to interact with game devices
7. Identify
uses of embedded computers
8. Differentiate
a port from a connector, identify various ports and connectors, and
differentiate among Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and NFC wireless device connections
9. Identify
safeguards against hardware theft and vandalism and hardware failure
10. Discuss
ways to prevent health-related injuries and disorders caused from technology
use, and describe ways to design a workplace ergonomically
COMPUTERS AND MOBILE
DEVICES
1. Types
of computers include:
2. Desktop
and mobile computers
3. Servers
and terminals
4. Smartphones,
digital cameras, e-book readers and portable media players
5. Game
devices
6. Embedded
computers
DESKTOPS AND MOBILE
COMPUTERS
Personal
computer (PC) - a computer that can perform all of its
input, processing, output, and storage activities by itself and is intended to
be used by one person at a time.
Desktop/desktop
computer - a personal computer designed to be in
a stationary location, where all of its components fit on or under a desk or
table
Laptop/notebook
computer - a thin, lightweight mobile computer
with a screen in its lid and a keyboard in its base
Tablet
- a thin, lightweight mobile computer that has a touch screen
Handheld
computer - a computer small enough to fit in one
hand
SERVERS
Server
- a computer dedicated to providing one or more services to other computers or
devices on a network
·
Rack server
·
Blade server
·
Tower server
SUPERCOMPUTERS
A
supercomputer
- the
fastest, most powerful computer and the most expensive
Server Vs Supercomputer
SERVER
|
SUPERCOMPUTER
|
Serves bits and bytes of data
that enter and leave the server
|
Regular hardware combined in enormous
proportions
|
Web servers-processing requests from surfers and
sending them back data
|
Contain so many processors
|
Web browsers -
assemble that data to generate Web pages
|
Predict the weather, build airplanes,
model the brain and simulate the way the
planet works.
|
Server send files in a network.
|
Sequoia Blue Gene/Q supercomputer processing
504 billion events per second(2013) ≈1 million
desktop computers.
|
TERMINALS
Terminal - a
computer, usually with limited processing power, that enables users to send
data to and/or receive information from a server, or host computer.
ATM
(automated teller machine)
- a
self-service banking terminal that connects to a host computer through a
network
CLOUD COMPUTING
Cloud
computing refers to an environment of servers
that house and provide access to resources users access through the Internet
MOBILE DEVICES
Smartphone - an
Internet-capable phone that usually also includes a calendar, an appointment
book, an address book, a calculator, a notepad, games, browser, and numerous
other apps
Digital
camera - a mobile device that allows users to take photos
and store the photographed images digitally
Portable
media player, sometimes called a personal media player -
a mobile device on which you can store, organize, and play or view digital
media
e-book
reader (short for electronic book reader), or e-reader
- a mobile device that is used primarily for reading e-books and other digital
publications
GAME DEVICES
Game
console - A mobile computing device designed
for single-player or multiplayer video games.
Handheld
game device - A small mobile device that contains a
screen, speakers, controls, and game console all in one unit.
EMBEDDED COMPUTERS
Embedded
computer
- A
special-purpose computer that functions as a component in a larger product.
·
Consumer electronics
·
Home automation devices
·
Automobiles
·
Process controllers and robotics
·
Computer devices and office machines
PORTS AND CONNECTIONS
Port -
the point at which a peripheral device attaches to or communicates with a
computer or mobile device so that the peripheral device can send data to or
receive information from the computer or mobile device
connector
joins a cable to a port. A connector at one end of a
cable attaches to a port on the computer or mobile device, and a connector at
the other end of the cable attaches to a port on the peripheral device
USB
port, short for universal serial bus port, can connect up
to 127 different peripheral devices together with a single connector. Instead
of connecting peripheral devices directly to ports on a mobile computer, some
mobile users prefer the flexibility of port replicators or docking stations
Instead
of connecting computers and mobile devices
to peripheral devices with a cable, some peripheral devices use wireless
communications technologies
·
WIFI
·
Bluetooth
·
NFC
PROTECTING HARDWARE
Hardware
can fail for a variety of reasons: aging hardware; random events such as
electrical power problems; and even errors in programs or apps
·
Undervoltage
·
Overvoltage or power surge
Surge
protector, also called a surge suppressor -
Uses electrical components to provide a stable current flow and minimize the
chances of an overvoltage reaching the computer and other electronic equipment
HEALTH CONCERNS OF
USING TECHNOLOGY
Uninterruptible
power supply (UPS) - a device that contains surge
protection circuits and one or more batteries that can provide power during a
temporary or permanent loss of power
Repetitive
strain injury (RSI) - An injury or disorder of the
muscles, nerves, tendons, ligaments, and joints
Computer
vision syndrome (CVS) - A technology-related health
condition that affects eyesight
Ergonomics
- An applied science devoted to incorporating comfort, efficiency, and safety
into the design of items in the workplace
Technology addiction occurs when the
technology consumes someone’s entire social life
MICROSOFT WORD
The Objectives At The End Of This Study Are:
- Knowing how to build a simple letter-based document that contains text elemen
- Build a simple letter-based document with existing editing elements in microsoft word 2010
- To build the merge mail perfectly and correctly
HOW TO PRINT CERTIFICATE CERTIFICATE AND MAJOR MAIL MERGE TECHNICAL
This is how print certificates are very practical for you who want to print certificates in bulk.
1. OPEN MICROSOFT WORD
Open Microsoft Word and create the certificate templates you want to print. Here is the template for the certificate to be printed later.
The NAME and INTRODUCTION CARD sections are left blank as we will automatically associate names with Microsoft Excel.
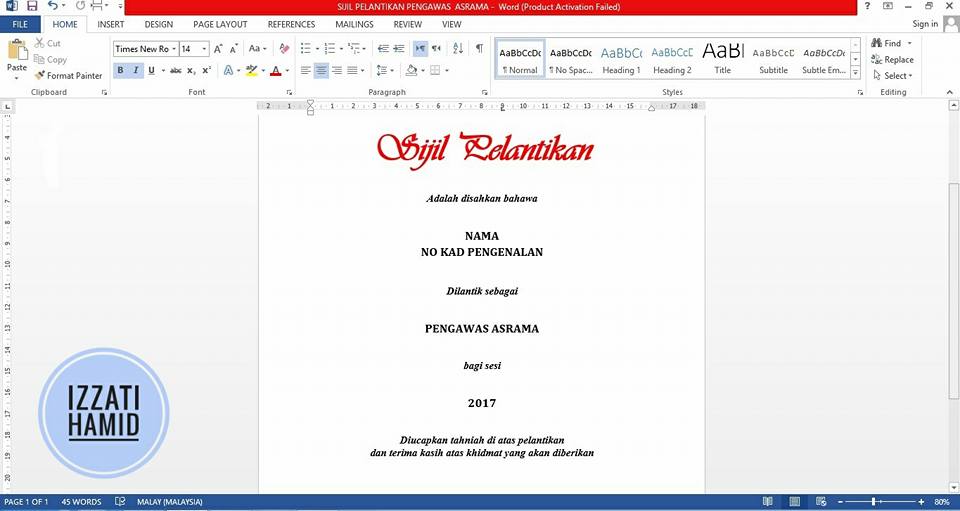
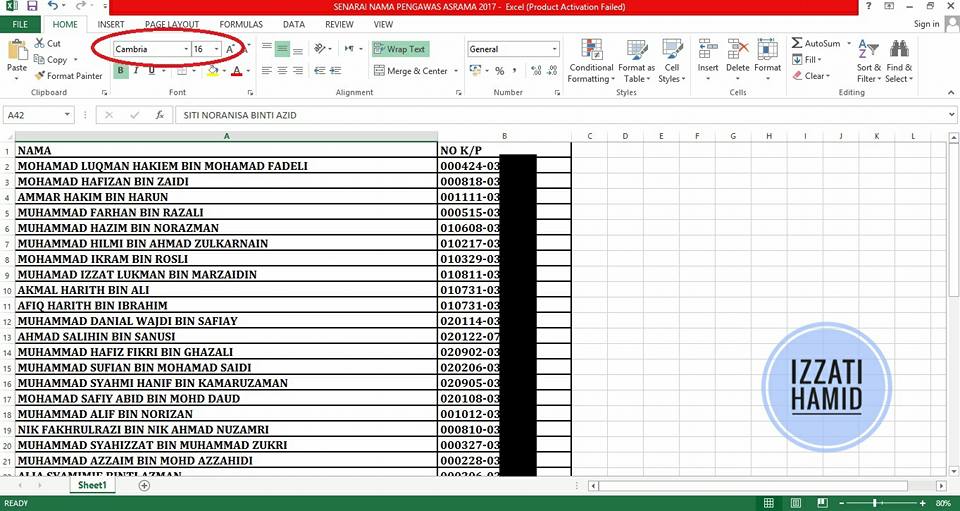
2. OPEN MICROSOFT EXCEL
Open Microsoft Excel and 'copy' ready-made names and identification numbers. Then, Save.
The purpose of making this list is to make it a database of the certificate templates that have been created.
The font and size of the text if it does not change is okay, but get the setting in Word later yes.
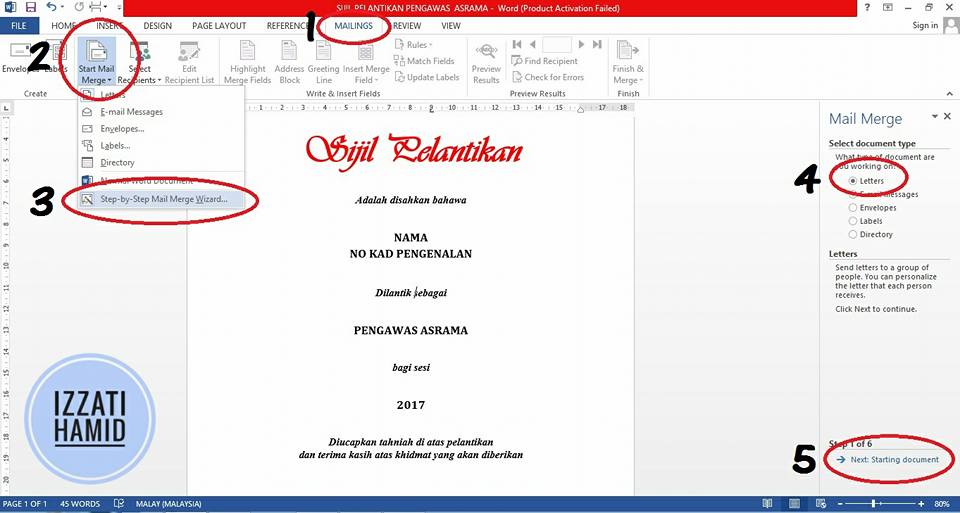
3. START 'MAIL MERGE' IN MICROSOFT WORD
The backend is near the Microsoft Word file with the certificate template.
Select:
"MAILINGS",
"START MAIL MERGE",
Click "STEP-BY-STEP MAIL MERGE WIZARD"
Select "LETTERS"
Click "NEXT: STARTING DOCUMENT"
Select "USE THE CURRENT DOCUMENT"
Click "NEXT: SELECT RECIPIENTS"
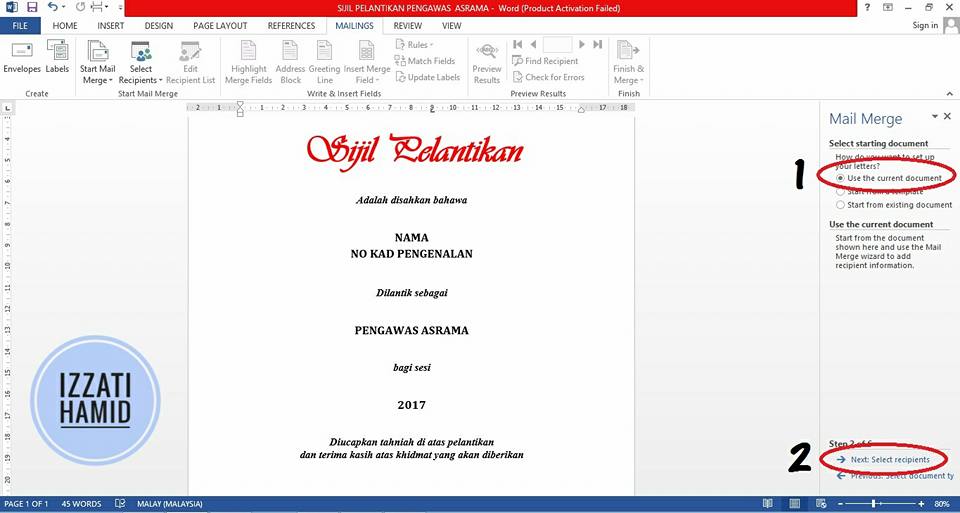
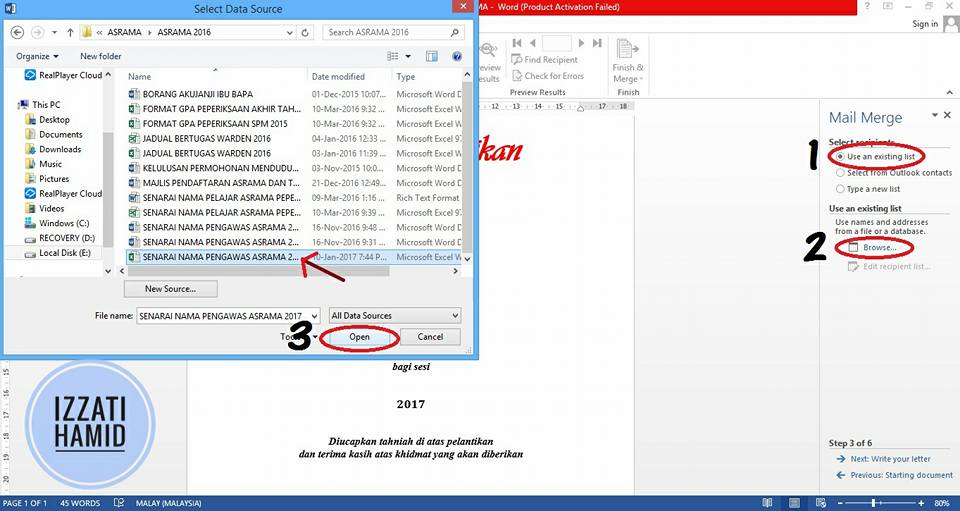
4. Select the FAIL MICROSOFT EXCEL LIST
Next, we will connect the student name list in Microsoft Excel with the certificate template that was created in Microsoft Word.
Select "USE AN EXISTING LIST".
Press "BROWSE".
Select the Name List to print.
Click "OPEN".
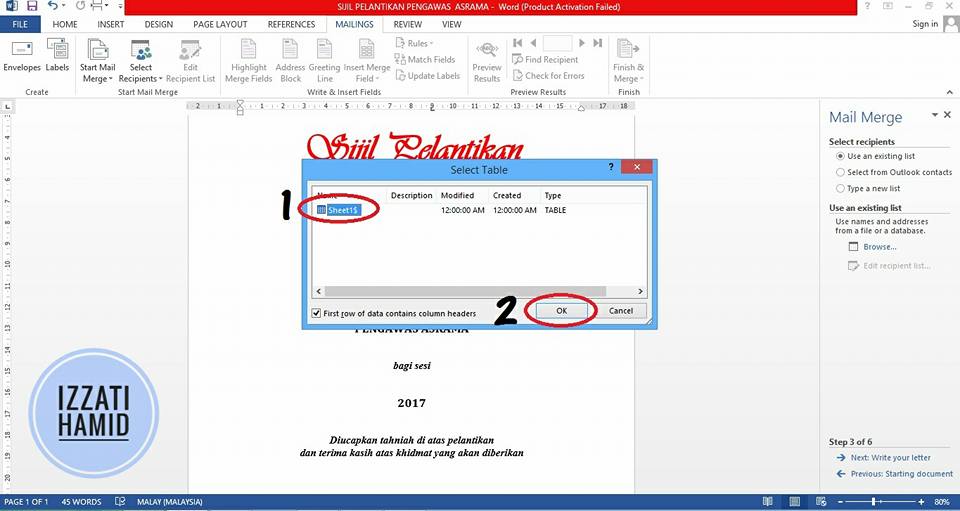
Select the "SHEET" name created in Microsoft Excel.
Click "OK".
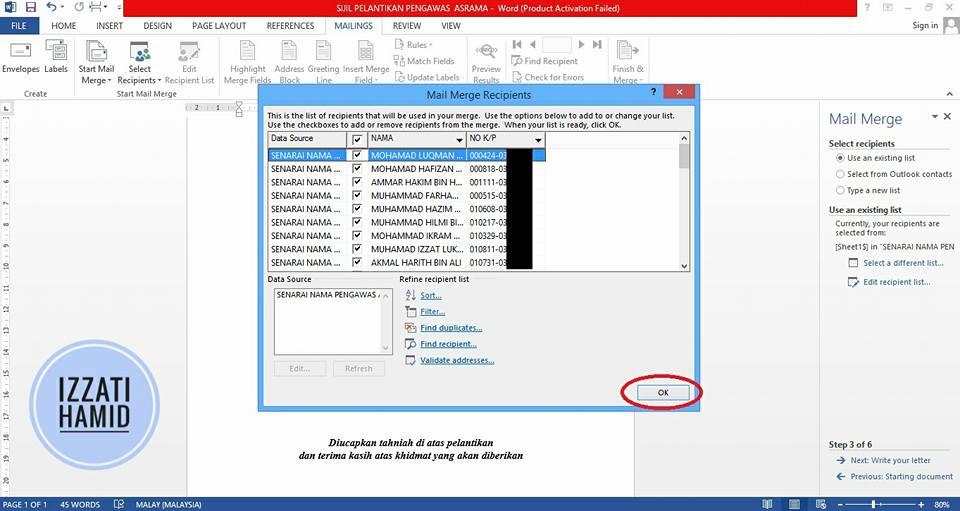
Will go out like this. Click "OK".
5. MERGE' DATA
Now, the list has been linked to this certificate template. Next, we will 'merge' the data in NAME and NO sections. CARD INTRODUCTION one by one.
Click "NEXT: WRITE YOUR LETTER"
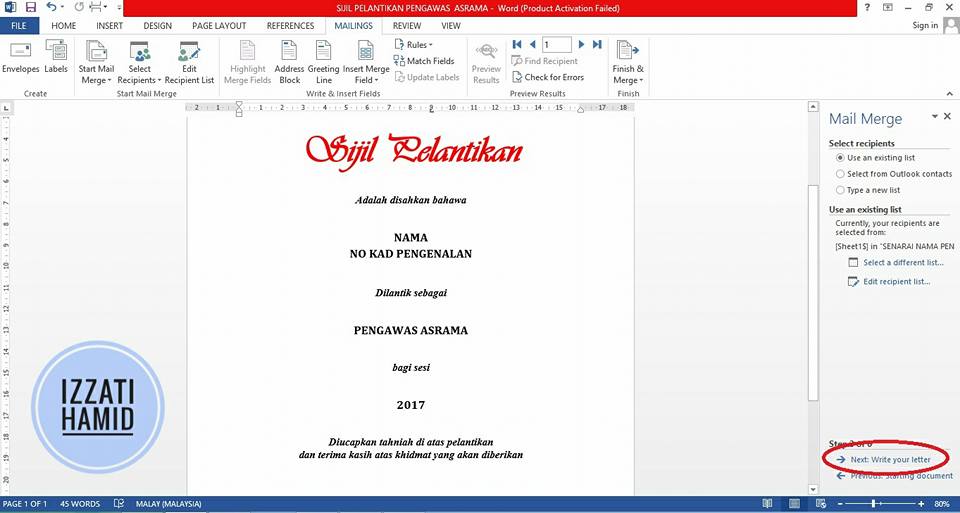
'Select'Name word on certificate.
Click "MORE ITEMS".
Select NAME.
Click "INSERT".
Press "CLOSE".
Now, the data contained under the 'row' NAME in Microsoft Excel has been linked to this template.
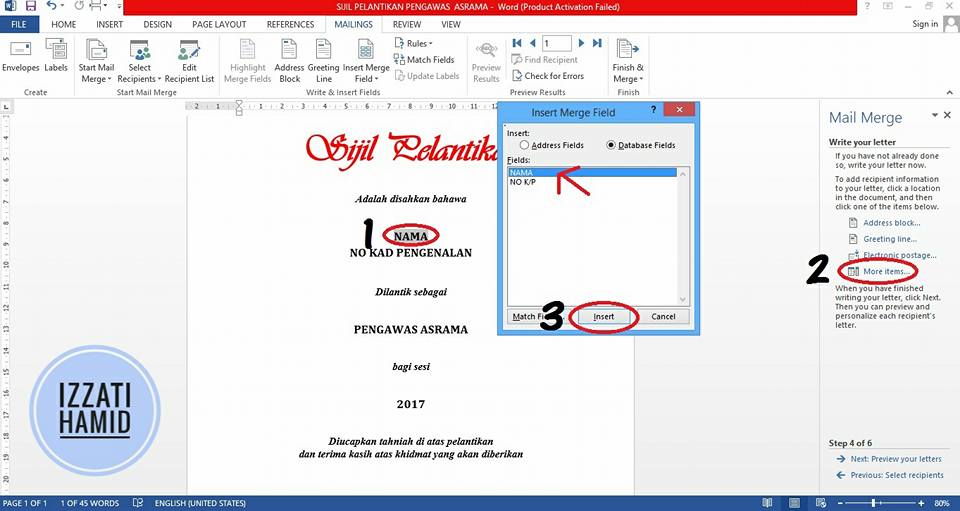
Repeat the same steps for word NO. IDENTIFICATION CARD.
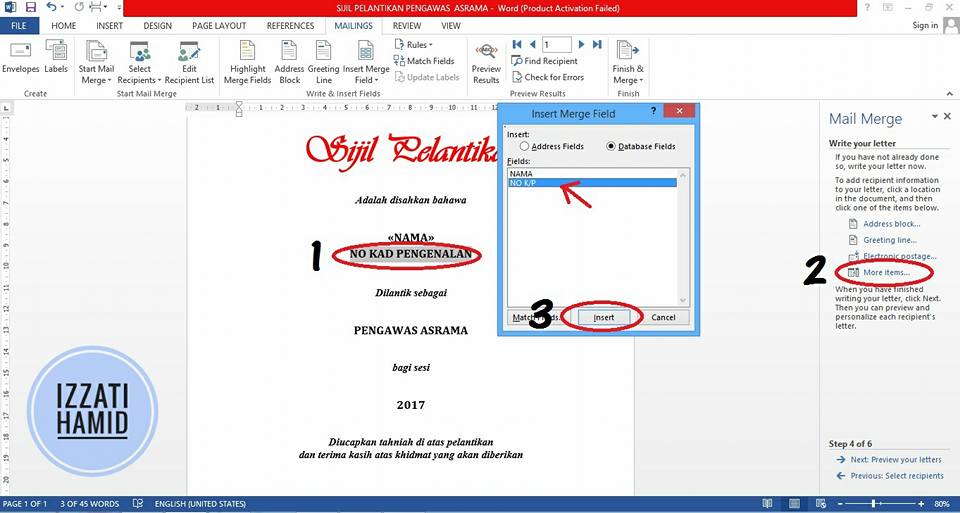 6. PREVIEW
6. PREVIEWClick "NEXT: PREVIEW YOUR LETTERS"
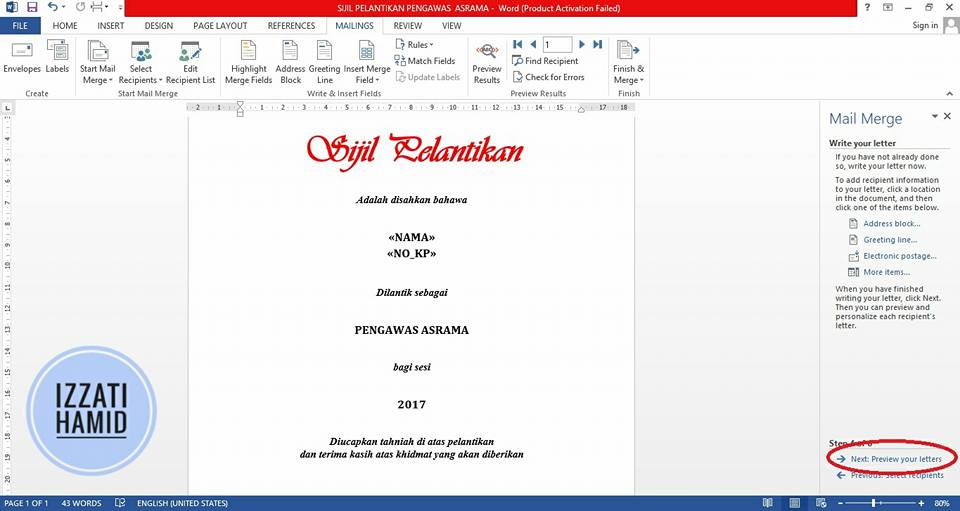 Click "NEXT: COMPLETE THE MERGE"
Click "NEXT: COMPLETE THE MERGE"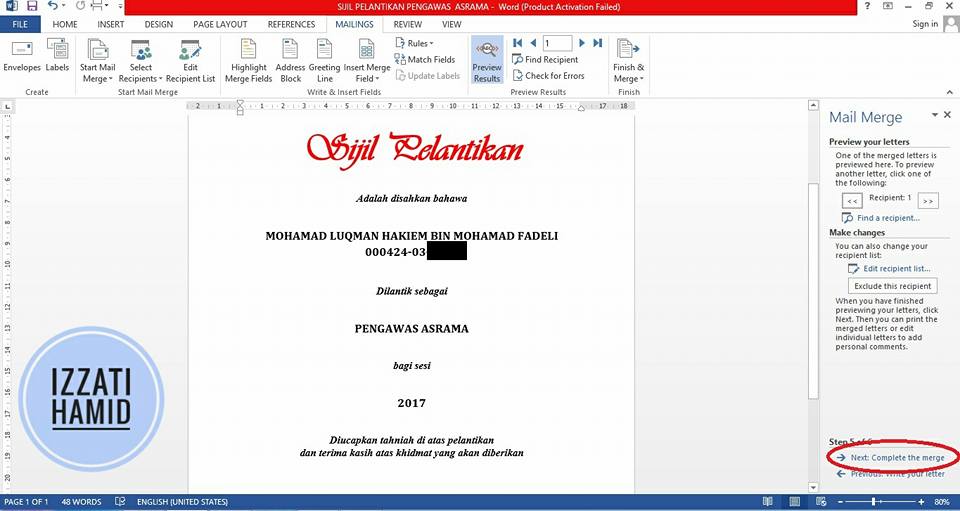
how-to print-certificate-13
7. PRINT
Now, all the data has been set in the template and is ready to be printed.
If you're sure, click "PRINT". If it's a taste, try printing on plain paper first.
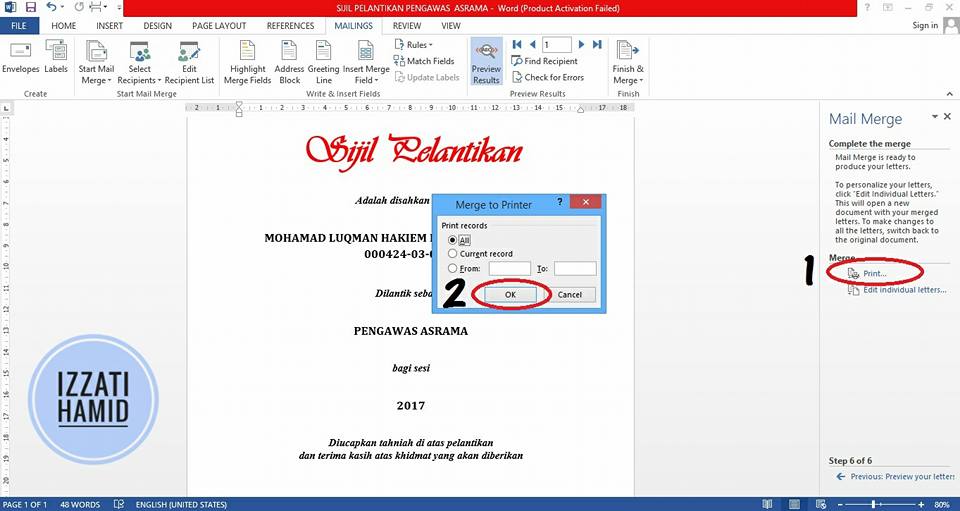
If there are too many certificates to print, make it half-way. The fear of 'printer' is getting stuck later.





No comments:
Post a Comment